What Is A A Bunionectomy?
Overview
 Bunion deformities are often part of a more generalized problem related to improper foot motion as you walk. The name for this is "pronation". Wearing orthotics can slow the progress of a bunion deformity. There are presently over 25 types of bunion procedures performed today. The choice of procedure is based on many factors including age, medical history, physical exam, and x-ray evaluation.
Bunion deformities are often part of a more generalized problem related to improper foot motion as you walk. The name for this is "pronation". Wearing orthotics can slow the progress of a bunion deformity. There are presently over 25 types of bunion procedures performed today. The choice of procedure is based on many factors including age, medical history, physical exam, and x-ray evaluation.
Causes
Women tend to suffer from bunions more often than men, probably because of the shoes they wear. But besides shoes, standing on the feet for long periods of time can also make symptoms of a bunion worse. Along with the bump, these bunion symptoms include pain or soreness, swelling, redness around the joint, a burning sensation or sometimes numbness. The big toe may develop calluses or not be able to move as well as it once did. Sores between the toes and ingrown toenails may also occur because of a bunion.
Symptoms
Often the bunion is not painful and the individual leads a normal active life. Other times the bunion can be very painful, even debilitating. Pain is usually very achy and typically radiates to the toes and along the arch of the foot. Due to the abnormal positioning of the bones in the foot, sharp nerve pains could also be present.
Diagnosis
Orthopaedic surgeons diagnose bunions on the basis of physical examination and weight bearing x-rays. Two angles are assessed, the intermetatarsal angle, that is between the first and second metatarsals (the bones that lead up to the base of the toes). If this angle exceeds 9? (the angle found in the healthy foot) it is abnormal and referred to as metatarsus primus varus. the hallux valgus angle, that is, the angle of the big toe as it drifts toward the small toe. An angle that exceeds 15? is considered to be a sign of pathology.
Non Surgical Treatment
Sometimes observation of the bunion is all that's needed. A periodic evaluation and x-ray examination can determine if your bunion deformity is advancing, thereby reducing your chance of irreversible damage to the joint. In many other cases however some type of treatment is needed. Early treatments are aimed at limiting the progression of the deformity and easing the pain of the bunion or an associated joint. Conservative treatments such as orthotics can achieve this but they won't reverse the deformity itself. These options include changes in shoe wear. Foot Mechanics Podiatrists are experts in shoe recommendation. Padding. Pads placed over the area of the bunion can help minimise pain, but will not stop the progression of the bunion. Activity modifications. Avoid activity that causes bunion pain, this could include standing for long periods of time. Medications. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen may help to relieve pain. Icing. Applying an ice pack several times a day helps reduce inflammation and pain. Orthotic devices. Orthotics are the mainstay of non-surgical treatment for bunions. 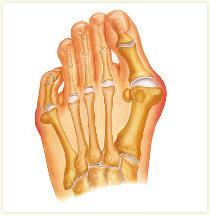
Surgical Treatment
Surgery can be a very successful treatment for bunions and could be considered if you are having pain that is affecting your function on a regular basis, for instance, pain during sports or wearing work shoes. It is important, however, that you are seen by a consultant orthopaedic foot and ankle surgeon who has undergone specialist training with a foot and ankle fellowship. There are many different surgical techniques and it is important that your surgeon is expert in several of these so that you have the one that is best for your unique deformity. Bunion removal is usually done under general anesthesia. This means you will be asleep throughout the procedure. The operation can be performed as a day-case, but an overnight stay in hospital is sometimes required. Your surgeon will explain the benefits and risks of having bunion surgery, and will also discuss the alternatives treatments.